作为一个技术音频,根据实际项目帮助团队制作各种优化工作流的工具是非常重要的工作内容。本文将以官方文档的示例为引子并结合 3 个 Wwise 小工具,展开说说我的 Wwise 底层学习之路。制作这些工具需要掌握基础的 Python 编程以及对 PySimplyGUI 这个库的使用来完成交互图形界面的搭建,还需要熟悉 Wwise 的基本概念和操作使用,这些部分的内容不会在文中详细展开。
从官方例子开始
当你想要为音频设计师们优化工作流中 Wwise 部分繁琐的重复性工作时,需要解决的第一个问题就是:如何让我们的程序和 Wwise 工程建立通信,获取想要的相关信息并调用 WAAPI(Wwise Authoring API)。
建立通信
有三种协议可与 Wwise 建立通信,包括:WAMP、 HTTP POST 或是在 Wwise 插件中调用 AK::Wwise::Plugin::Host::WaapiCall()。其中 WAMP(The Web Application Messaging Protocol) 协议的性能最佳,且支持远程过程调用(RPC)和发布订阅功能,因此通常选择这一协议。
官方文档中对 WAMP 是什么作了补充说明:WAMP 旨在连接分布式应用中的应用组件。WAMP 使用 WebSocket 作为其默认传输方式,允许有序、可靠、双向、信息为导向的通信。 WAMP 允许客户端使用 JSON 参数来调用函数并获取结构性 JSON 结果。
另外,利用 WAMP 协议调用 API 的可选编程语言有多种,官方推荐的有:C++、C、Python3.6+,我们结合一个官方 Python3.6+ 的示例代码来说明:
-
在当前 Python 环境下安装如下依赖
1
py -3 -m pip install waapi-client
-
导入依赖,建立通信
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
# 导入 WAAPI 相关依赖 from waapi import WaapiClient, CannotConnectToWaapiException from pprint import pprint # try except 作为连接失败的异常处理 try: # 使用 URL 连接 WAAPI,这里显式写出了默认地址和端口,可以根据需要在 Wwise 中自行修改端口 # 此外使用 with as 能保证代码运行至最后自动断开程序和 WAAPI 的连接 with WaapiClient(url='ws://127.0.0.1:8080/waapi') as client: ''' JSON-RPC: JSON-Remote Procedure Call ''' except CannotConnectToWaapiException: print("Could not connect to Waapi: Is Wwise running and Wwise Authoring API enabled?")
根据上面代码段中的注释我们得以了解通信是如何被建立的,现在终于来到了最后一部分,我们来看看例子中是如何通过 RPC 调用 API 获得要想的信息,实现各种客制化的功能。
调用 API
程序运行结果:
首先让我们回到上面曾提到过的两个定义,远程过程调用和发布订阅,它们也分别对应了通过 WAMP 协议支持的两种通信方式:
-
远程过程调用 - client.call()
允许针对 Wwise 设计工具远程调用函数,我们可以在程序中调用官方 reference 给出的 Functions 中的所有 API。调用这些 API 后我们可以直接获取几乎所有 Wwise 对象的诸多属性,并对它们做出各种操作,我们的第一个工具就是在此基础上实现的。
-
发布订阅 - client.subscribe()
允许在 Wwise 设计工具中出现变动时接收通知,我们可以在程序中调用官方 reference 给出的 Topics 中的所有 API。调用这些 API 后我们可以订阅 Wwise 中对应的动作,比如订阅某个对象的名称,当它的名称修改后就能得到返回的具体信息。
再次回到官方示例中使用到的两个 API,它们都属于 Fuctions 类,下面是之前代码被省去的部分:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
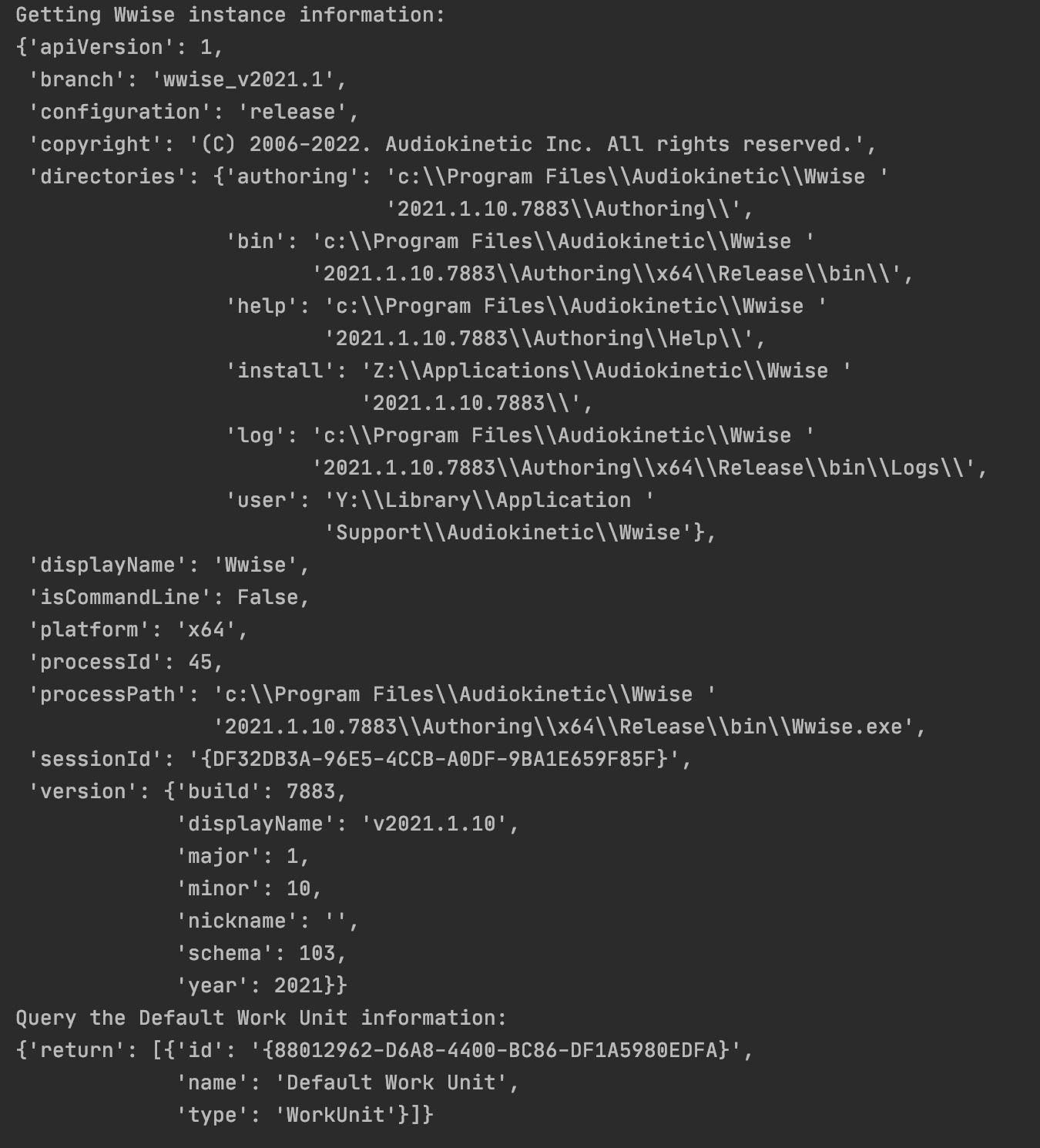
# 获取工程信息,无参数调用
print("Getting Wwise instance information:")
result = client.call("ak.wwise.core.getInfo")
pprint(result)
# 查询指定对象的信息 ,JSON 参数调用
print("Query the Default Work Unit information:")
# JSON 参数段
object_get_args = {
"from": {
"path": ["\\Actor-Mixer Hierarchy\\Default Work Unit"]
},
"options": {
"return": ["id", "name", "type"]
}
}
result = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.get", object_get_args)
pprint(result)
可以看到代码中我们通过ak.wwise.core.getInfo获取了当前 Wwise 工程的全局信息;通过ak.wwise.core.object.get查询到了一个指定路径下默认工作单元的基本信息(通过这个 API 可以获取 Wwise 内任意对象的信息),这个 API 需要在调用时提供对应 JSON 格式的参数。这里参数中的 “path” 属于 Augments 参数,规定了调用此 API 需要提供的参数;”return” 属于 Options 参数,手动规定了调用后返回结果的具体内容,具体的信息我们可以在官方文档相关页对应的语法(Schema)中查看。
至此我们终于到达了 Wwise SDK 的核心部分 —— WAAPI。
用例示例
Wwise Authoring API 可以和以下项目集成:
- 游戏引擎
- 对话管理管线
- 用于声音设计、编辑、对话录音或音乐制作的 DAW
- 各种各样的脚本
The Wwise Authoring API 可以用于:
- 任务自动化,如导入音频文件或创建 Wwise 对象
- 在移动设备上远程控制 Wwise
- 实现自定义 Wwise 界面
- 向 Wwise 添加自定义功能。请参阅 定义命令扩展 。
工作原理
WAAPI 是一种允许其他进程与 Wwise 设计工具进行通信的 API。WAAPI 支持双向通信,允许进程进行远程程序调用并订阅相关主题,以便在 Wwise 中出现变动时及时获悉。
WAAPI 允许访问三个不同层次的功能:
- Wwise 用户界面:视图、选项、命令等
- Wwise 设计工具核心:工程和对象、SoundBank、音频文件、走带等
- Wwise 声音引擎:Game Object、Post Event、RTPC Value 等
WAAPI 可通过各种编程语言来使用。
Wwise 的官方文档强大且全面,但 WAAPI 的部分是按字典序分类排列的,且不存在关联性缺乏整理,对于初学者非常不友好。受到溪夜老师的文章人人都能用 WAAPI(一)概述启发,我在过文档学习各 API 功能的过程中尝试去使用思维导图对它们进行整理分类。
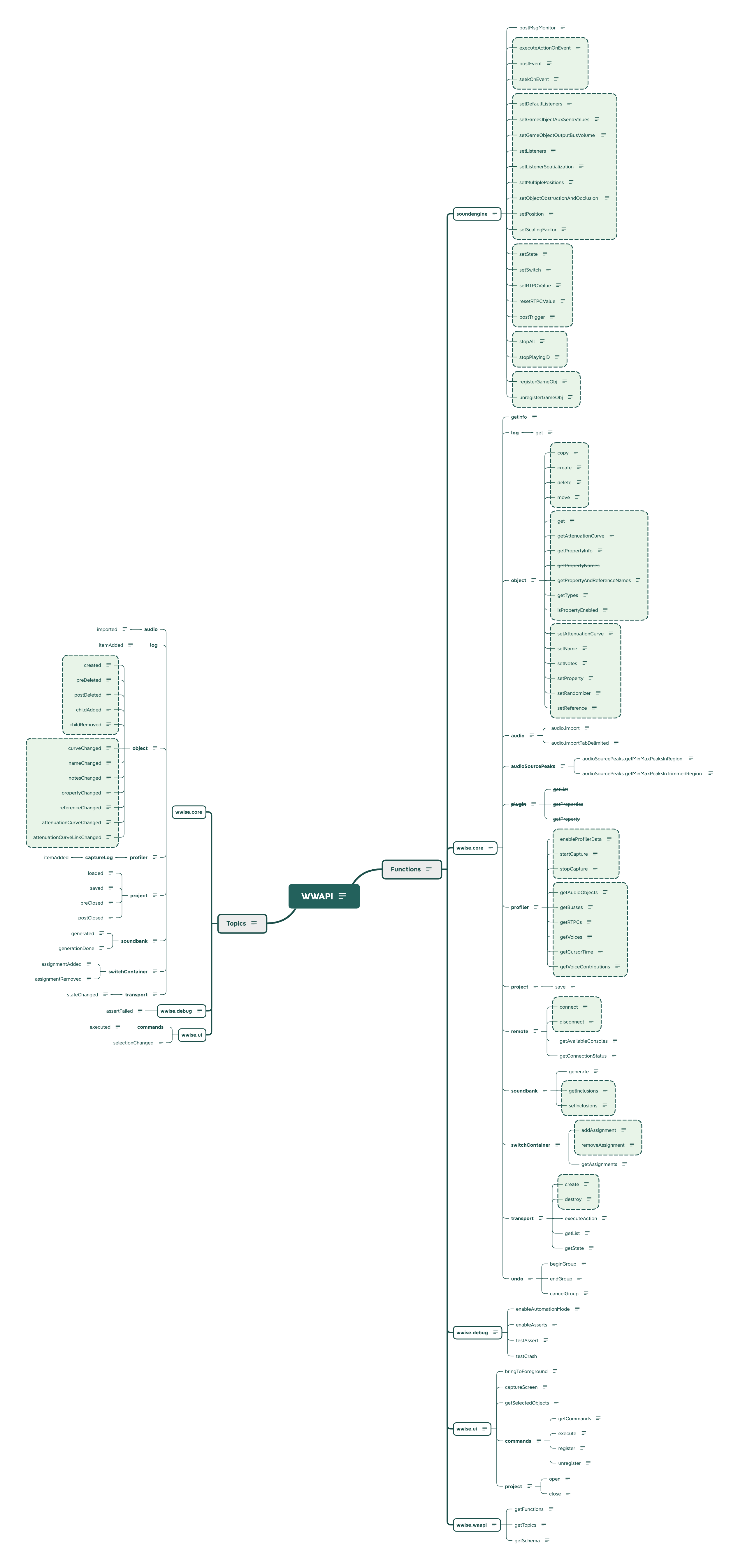
如上图所示,按照远程过程调用和发布订阅的差异,官方文档将 WAAPI 分为 Fuctions 和 Topics 两大类,再按照类的命名我们还可以对所有的 API 进一步细分。图中的各个绿色虚线框是针对每个 API 的实际功能进行的更细致的分类。除了上述的分类方法,我们还可以按有无输入参数,有无返回值来分类。应用范围较广的 API 都有着对应的官方示例,利用好这些示例可以帮助我们快速熟悉这些 API。对于没有示例的 API,除了查看官方文档中对其功能简单的描述外,还要仔细查看它的参数以及返回值,以便判断它可能的应用场景。
为选中的对象创建 SoundBank
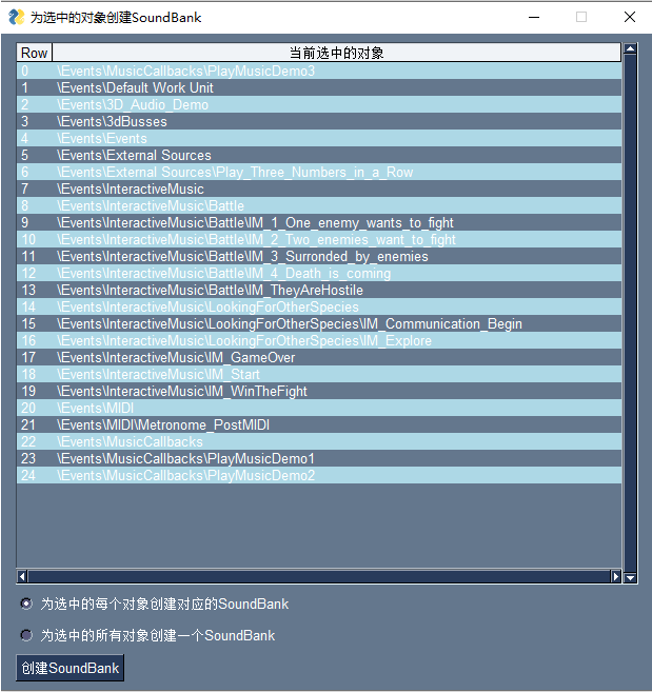
在实际项目中,经常存在需要为大量 Event 创建不同 SoundBank 的情况,我们可以通过调用 WAAPI 实现客制化工具来优化这一流程。上图是这个工具的界面,程序会自动识别当前 Wwise 工程中用户在 Event 选项卡下选中的对象,并根据对象的路径以及单选按钮中的限制条件为这些对象创建对应的 SoundBank。下面将这个工具分为:选中对象的获取和判断,不同生成条件下的路径判断和 SoundBank 生成三两部分,结合代码展开讲解。
选中对象的获取和判断
首先明确我们所需要的 API,这里显然是需要获取 UI 层面的信息,我们定位到文档的 ak.wwise.ui 部分并选择 ak.wwise.ui.getSelectedObjects 。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 获取当前选中对象的以下四种信息
opts_select = {
"return": [
"id", "path", "name", "type"
]
}
ids = [] # 所有选中对象的id
# 三种路径主要是为了处理选中对象后在SoundBanks下生成对应路径的问题
ori_paths = [] # 所有选中对象的工程路径
paths = [] # 所有选中对象应在SoundBanks下的路径
parent_paths = [] # 所有选中对象应在SoundBanks下的父路径
names = [] # 所有选中对象的名称
types = [] # 所有选中对象的类型
wrong_select = False # 用于判断选中对象的合法性
same_path = False # 用于判断所有选中对象是否处于同一父路径下
# 调用 API 获取所需对象
result_select = client.call("ak.wwise.ui.getSelectedObjects", options=opts_select)['objects']
for select in result_select:
# 判断选中对象是否合法,即是否在Event路径下
if select.get('path')[:6] != '\\Event':
wrong_select = True
break
ids.append(select.get('id'))
names.append(select.get('name'))
ori_paths.append(select.get('path'))
types.append(select.get('type'))
# 修改选中对象的路径为\SoundBanks开头
path = '\SoundBanks' + select.get('path')[7:]
paths.append(path)
# 获取父级路径
name = select.get('name')
name = '\\' + name
parent_path = path.replace(name, "")
parent_paths.append(parent_path)
通过上面的代码,我们成功获取了 Wwise 工程中选中对象的所需信息,判断了合法性且对路径信息进行了处理以便后续的操作。要注意的是我们通过设置 options 参数以筛选获得必要的四种信息。另外,我们在初次获取信息并创建好 GUI window 显示后,可以把上面的代码放入 while 循环中,通过window.read()和window['-TABLE-'].update(values=data)来保证 table 中选中信息的实时刷新。
生成条件下的路径判断和 SoundBank 生成
下面以为所有选中对象创建一个 SoundBank 的代码为例,另一选项需要的是更多对不同路径逻辑上的判断,在 WAAPI 的使用上是基本一致的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
# 为选中的所有对象创建一个SoundBank,传入的参数是每个对象的父路径以及 id
def create_for_all_event(p_paths, object_ids):
path_split = p_paths[0].replace('\\', "", 1)
path_split = path_split.split('\\')
path_split[0] = 'Events'
# 如果所有对象在同一路径下
if same_path and len(path_split) > 1:
cur_event_path = '\\' + path_split[0]
# 从根部开始逐一判断每一级父路径的类型并在SoundBank下创建
for cur in path_split[1:]:
cur_soundbank_path = '\\SoundBanks' + cur_event_path[7:]
cur_event_path = cur_event_path + '\\' + cur
# 查询当前一级对象的类型
args_get_cur_type = {
"from": {
"path": [
cur_event_path
]
}
}
opts_get_cur_type = {
"return": [
"type"
]
}
cur_type = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.get", args_get_cur_type, options=opts_get_cur_type)['return'][0].get('type')
# 根据查询到的类型创建对应对象
args_create_path = {
"parent": cur_soundbank_path,
"type": cur_type,
"name": cur,
"onNameConflict": "merge"
}
client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.create", args_create_path)
bank_path = '\\SoundBanks' + cur_event_path[7:]
# 不在同一路径下时以Default Work Unit为默认路径
else:
bank_path = "\\SoundBanks\\Default Work Unit"
# 创建Bank
args_create_bank = {
"parent": bank_path,
"type": "SoundBank",
"name": "ALL_IN_ONE",
"onNameConflict": "rename"
}
result_bank_id = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.create", args_create_bank).get('id')
# 将选中的所有Event添加至Bank
for object_id in object_ids:
args_bank_add = {
"soundbank": result_bank_id,
"operation": "add",
"inclusions": [
{
"object": object_id,
"filter": [
"events"
]
}
]
}
client.call("ak.wwise.core.soundbank.setInclusions", args_bank_add)
上面的代码保存了 Events 选项卡下各对象的父路径,从根部开始依次遍历判断类型并使用ak.wwise.core.object.create API 在 SoundBanks 选项卡下生成对应的对象,如此成功复制了选中对象的路径层级。再在这个路径下使用相同的 API 生成 Bank,由于此时生成的 Bank 不包含任何 Inclusions,我们还需要调用ak.wwise.core.soundbank.setInclusions将 选中的所有 Events 添加进去。
使用命令扩展将程序嵌入 Wwise 菜单
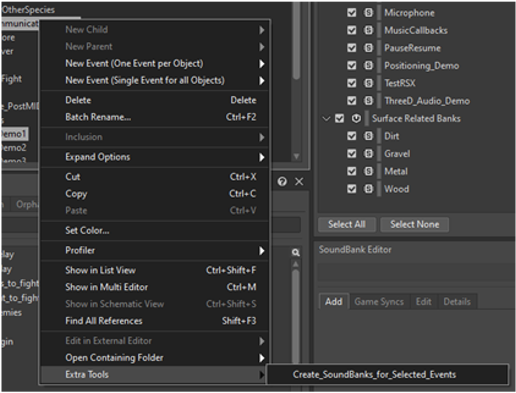
对于使用频率比较高的工具,我们可以使用命令扩展将其嵌入 Wwise 客户端。如上图我们将这个工具嵌入至了 Wwise Events 选项卡的右键菜单中,使用工具时更方便快捷。
命令扩展概述
命令扩展方便为 Wwise 设计工具定义新的命令。每个命令都与 Wwise 触发的外部程序关联。所执行的程序可接收来自当前所选对象的各种预定义参数。
可通过不同方式触发扩展命令:
- 键盘快捷方式
- 上下文菜单
- 主菜单
- 控制器
- WAAPI(使用
ak.wwise.ui.commands.execute)可在多个级别定义扩展命令:
- 用户数据目录中:
- Windows:”%APPDATA%\Audiokinetic\Wwise\Add-ons\Commands”
- macOS:”$HOME/Library/Application Support/Audiokinetic/Wwise/Add-ons/Commands”
- 安装文件夹中:
- Windows:”%WWISEROOT%\Authoring\Data\Add-ons\Commands”
- macOS:”/Library/Application Support/Audiokinetic/Wwise
/Authoring/Data/Add-ons/Commands" - 工程文件夹中:Add-ons\Commands 下
- 使用
ak.wwise.ui.commands.register
针对音频工作者最常使用的 Windows 和 Mac 系统,可以使用 pyinstaller、py2app 之类的库将程序打包为对应平台的工具。根据使用场景,我们可以选择将扩展命令的 JSON 文件放至不同的层级下,考虑到当前工具的泛用性,我们可以选择放至其安装文件夹或用户数据目录中,对于一些针对性强的项目级工具可以放至工程文件夹中。另外我们还可以编写脚本实现将扩展命令和工具自动放至所需的目录的操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
{
"version":2,
"commands":[
{
"id":"off.create_soundbanks_for_selected_events",
"displayName":"Create SoundBanks for Selected Events",
"program":"/tool1.app",
"args":"",
"startMode":"MultipleSelectionSingleProcessSpaceSeparated",
"cwd":"${CurrentCommandDirectory}",
"contextMenu": {
"basePath":"Extra tools",
"enabledFor":"Event, WorkUnit, Folder"
}
}
]
}
上面是我们将刚写好的生成 SoundBank 工具嵌入 Wwise 上下文菜单的 JSON 扩展命令代码,官方文档中对于扩展命令的定义字段抖做出了较详细的描述。
上面的命令中 cwd 字段对应了执行程序当前的工作目录,我们直接使用${CurrentCommandDirectory}这一官方定义的通用目录(当前扩展命令所在的路径); program 字段对应了需要运行的执行程序的路径,我们将其放在了同一路径下所以这里直接填写对应的文件名;args 字段是需要给执行程序传入的参数,这里为空;startMode 字段指定了在 Wwise UI 中执行多选时如何扩展参数字段中的变量,由于我们的工具存在选中多个对象的情况,所以填入值为 MultipleSelectionSingleProcessSpaceSeparated;因为可能存在多个扩展工具,我们在 contextMenu 字段中的 basePath 中填入所需的值作为一级菜单名,在 enabledFor 中限定允许激活此命令的对象,即只有 Event、WorkUnit 和 Folder对象的右键菜单才能使用此工具。
删除冗余的 wem 文件
通常一个进行的项目和 Wwise 工程是一对一的关系,随着项目的推进,我们需要定期清理一些 Wwise 工程中的冗余资源。下面从另一个角度聊聊 Wwise 底层相关的知识,涉及的工具只用到了极少的 WAAPI,关键的信息是直接从工程路径的相关的文件中或是通过某些文件夹下的文件本身,读取并处理得到的。
工程路径和 SoundBanksInfo.xml 文件
在生成 SoundBank 后,Wwise 工程路径下会出现一个名为 GeneratedSoundBanks 的文件夹,里面有生成后各平台的 Bank 文件、wem(Wwise Encoded Media) 文件以及 SoundBanksInfo.xml 文件,这个 xml 文件中保存了所有与 SoundBank 相关的信息。因此我们可以通过相关库读取 xml 文件并获得所有的已使用的 wem 文件的信息。由于存在多次生成 SoundBank 的情况,我们想要删除 GeneratedSoundBanks 文件夹中没有被使用到的冗余 wem 文件。
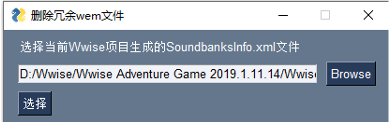
由于存在工程文件夹位置变更的情况,如上图所示,工具首先需要用户选择当前项目工程/平台对应的 xml 文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
<SoundBanksInfo Platform="Mac" BasePlatform="Mac" SchemaVersion="12" SoundbankVersion="140">
<RootPaths>
<ProjectRoot>/Users/dotm/Library/Application Support/Wwise2019/Bottles/Wwise2019x64/dosdevices/z:/Applications/Audiokinetic/Wwise 2021.1.10.7883/SampleProject/</ProjectRoot>
<SourceFilesRoot>/Users/dotm/Library/Application Support/Wwise2019/Bottles/Wwise2019x64/dosdevices/z:/Applications/Audiokinetic/Wwise 2021.1.10.7883/SampleProject/.cache/Windows/</SourceFilesRoot>
<SoundBanksRoot>/Users/dotm/Library/Application Support/Wwise2019/Bottles/Wwise2019x64/dosdevices/z:/Applications/Audiokinetic/Wwise 2021.1.10.7883/SampleProject/GeneratedSoundBanks/Windows/</SoundBanksRoot>
<ExternalSourcesInputFile></ExternalSourcesInputFile>
<ExternalSourcesOutputRoot>/Users/dotm/Library/Application Support/Wwise2019/Bottles/Wwise2019x64/dosdevices/z:/Applications/Audiokinetic/Wwise 2021.1.10.7883/SampleProject/GeneratedSoundBanks/Windows</ExternalSourcesOutputRoot>
</RootPaths>
<StreamedFiles>
<File Id="1001903680" Language="SFX">
<ShortName>NYC Ambience\OneShot_ThunderBkgrnd_02.wav</ShortName>
<Path>SFX/NYC Ambience/OneShot_ThunderBkgrnd_02_CC87FBFB.wem</Path>
</File>
</StreamedFiles>
<SoundBanks>
<SoundBank Id="85412153" Language="SFX" Hash="2355214421">
<ObjectPath>\SoundBanks\Ambience\Ambience</ObjectPath>
<ShortName>Ambience</ShortName>
<Path>Ambience.bnk</Path>
<IncludedEvents>
<Event Id="3339089830" Name="Play_24h_New_York_City_Ambience" ObjectPath="\Events\Ambience\Play_24h_New_York_City_Ambience">
<ReferencedStreamedFiles...>
<IncludedMemoryFiles...>
</Event>
</IncludedEvents>
</SoundBank>
</SoundBanks>
</SoundBanksInfo>
结合上方的例子,我们看看在 SoundBanksInfo.xml 文件中有哪些关键标签内的信息是我们需要的。当我们在 Wwise 中对较长的背景音乐等音频素材启用 stream 选项即流媒体播放后,在生成 SoundBank 时就会将这些媒体文件存储到对应的 wem 文件中以供在游戏当中进行流播放,
对比使用情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# 搜索xml中未使用的音频文件(对比<StreamedFiles>标签下的文件和<SoundBanksRoot>指向路径下的文件)
def search_unused_files(path):
soundbank_data = parse(path)
root_node = soundbank_data.documentElement
root_path = root_node.getElementsByTagName('SoundBanksRoot')[0].childNodes[0].data
file_list_used = []
file_list_unused = []
file_abspath_list_unused = []
nodes = root_node.getElementsByTagName('SoundBanks')
for node in nodes:
events = node.getElementsByTagName('IncludedEvents')
for event in events:
streamedFiles = event.getElementsByTagName('ReferencedStreamedFiles')
for streamedFile in streamedFiles:
files = streamedFile.getElementsByTagName('File')
for file in files:
file_id = str(file.getAttribute('Id'))
# 不同bank可能引用同一wem,去重复
if file_list_used.count(file_id) == 0:
file_list_used.append(file_id)
memoryFiles = event.getElementsByTagName('IncludedMemoryFiles')
for memoryFile in memoryFiles:
files = memoryFile.getElementsByTagName('File')
for file in files:
file_id = str(file.getAttribute('Id'))
# 不同bank可能引用同一wem,去重复
if file_list_used.count(file_id) == 0:
file_list_used.append(file_id)
# 读取<SoundBanksRoot>标签指向的路径下所有wem文件的路径
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(root_path):
for file in files:
base_name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
if ext == ".wem":
if file_list_used.count(base_name) == 0:
file_list_unused.append(file)
file_abspath_list_unused.append(os.path.join(root, file))
return file_list_unused, file_abspath_list_unused
对比 xml 文件中列出的所有引用到的 wem 文件和 GeneratedSoundBanks 文件夹下实际存在的 wem 文件即可得到未被使用的冗余文件列表,这里会使用到 xml.dom.minidom 这个库来处理 xml 文件。
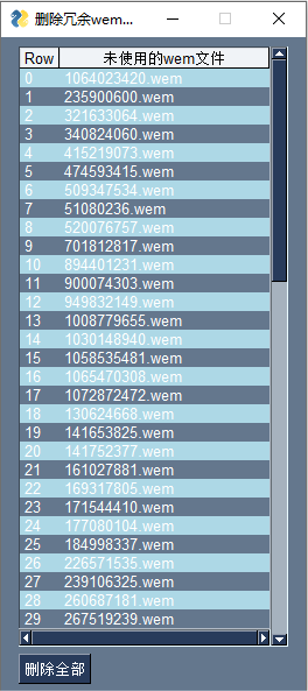
删除冗余的音频文件
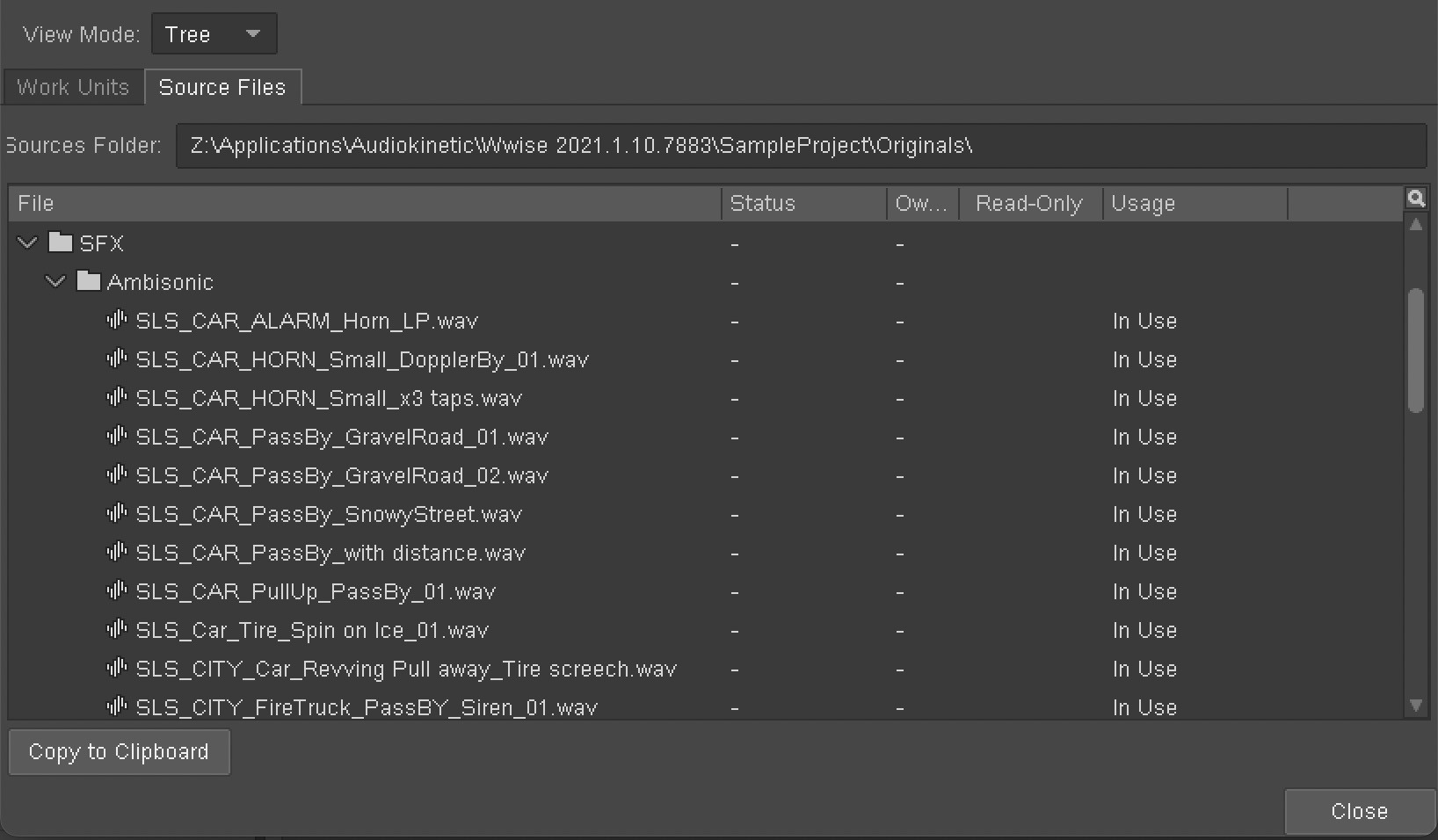
在 Wwise 客户端中打开 File Manager(Shift + F1),在 Source Files 选项卡中会显示各资源的使用情况,可以编写工具实现对 Usage 使用情况为 Not In Use 的冗余 SFX 资源的一键删除。
提高工具对 Wwise 版本的兼容性
随着 Wwise 版本升级至 2021,出现了 WAQL(Wwise Authoring Query Language) 优化了在 Wwise 客户端内或是底层代码层面对各种对象的搜索查询。但时常会出现项目由于稳定性等考虑,依然不得不维持在较早的版本,为了提高工具在不同版本下的兼容性,我们需要考虑新旧版本的差异,很多 WAAPI 的参数名都在新版本做了更新,比如:ak.wwise.core.object.get 这一 API 的 options 的 return 返回值在 21 版本就新增了originalWavFilePath 这一项,之前为 sound:originalWavFilePath。
Wwise Authoring Query Language (WAQL) 方便查询 Wwise 工程及其对象。藉此,用户可枚举各种 Wwise 对象(如 Sound、Container、Bus、Event 和 SoundBank),并按照属性(如名称、注释、ID、音量、音高和输出总线)加以筛选。另外,还可依据特定对象引用(如 Event 目标和输出总线)实施查询。
WAQL 可用于以下场合:
- Wwise 工具栏搜索
- List View 搜索
- Schematic View 搜索
- WAAPI(使用 ak.wwise.core.object.get 函数)
以下工具在启动时会先判断当前 Wwise 客户端的版本,并根据版本自动调用不同的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 获取当前Wwise版本
info_result = client.call("ak.wwise.core.getInfo").get('version')['displayName']
wwise_version = int(info_result.replace('v', '')[:4])
···
# 根据Wwise版本选择对应方法
if wwise_version < 2021:
wwu()
else:
waql()
搜索已使用的音频资源
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
# 获取当前工程路径
args_project = {
"from": {
"ofType": [
"Project"
]
}
}
opts_project = {
"return": [
"name",
"filePath"
]
}
result = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.get", args_project, options=opts_project)['return'][0]
name = '\\' + result.get('name') + '.wproj'
file_path = result.get('filePath')
project_path = file_path.replace(name, '') # 工程根路径
originals_path = project_path + '\\Originals' # 音频源文件路径
# 使用wwu方法(针对低于Wwise 2021的版本)
def wwu():
wwu_path1 = project_path + '\\Actor-Mixer Hierarchy'
wwu_path2 = project_path + '\\Interactive Music Hierarchy'
used_ids = []
# 遍历包含音频源文件的wwu文件(都在以下两个文件夹内)
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(wwu_path1):
for file in files:
base_name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
if ext == ".wwu":
wwu_data = parse(os.path.join(root, file))
root_node = wwu_data.documentElement
nodes = root_node.getElementsByTagName('AudioFileSource')
for node in nodes:
used_ids.append(node.getAttribute('ID'))
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(wwu_path2):
for file in files:
base_name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
if ext == ".wwu":
wwu_data = parse(os.path.join(root, file))
root_node = wwu_data.documentElement
nodes = root_node.getElementsByTagName('AudioFileSource')
for node in nodes:
used_ids.append(node.getAttribute('ID'))
# 根据wwu文件获得项目使用的音频资源的路径
args_wwu = {
"from": {
"id": used_ids
}
}
opts_wwu = {
"return": [
"name", "sound:originalWavFilePath"
]
}
used_paths = []
wwu_results = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.get", args_wwu, options=opts_wwu)['return']
for r in wwu_results:
used_paths.append(r.get('sound:originalWavFilePath'))
used_paths = list(set(used_paths))
if used_paths:
used_paths = [p.lower() for p in used_paths] # 对路径小写处理(由于WWAPI的bug,返回的路径大小写会出错)
unused_paths = get_unused_paths(used_paths)
gui(unused_paths)
wwu(Wwise Work Unit) 文件包含与工程中特定部分或元素相关的信息(本质是 xml 文件),我们先通过 WAAPI 获得当前工程的根路径,进而得到 Actor-Mixer Hierarchy 和 Interactive Music Hierarchy 这两个层级下的 wwu 文件。搜索这些文件就可以找到工程正在使用的音频文件的 id 信息,再通过这些 id 使用ak.wwise.core.object.get API 就可以找到这些文件的路径。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 使用WAQL方法(针对Wwise 2021及以上版本)
def waql():
args_all_audio = {
"waql": "$ from type audiofilesource"
}
opts_all_audio = {
"return": [
"originalWavFilePath",
"type"
]
}
results = client.call("ak.wwise.core.object.get", args_all_audio, options=opts_all_audio)['return']
# 由于返回的result是list嵌套dist,删除插件源等没有音频源的项返回的空字典并将dict转化为list
while {} in results:
results.remove({})
used_paths = []
for r in results:
used_paths.append(r.get('originalWavFilePath'))
used_paths = list(set(used_paths))
if used_paths:
used_paths = [p.lower() for p in used_paths] # 小写处理,理由同上
unused_paths = get_unused_paths(used_paths)
gui(unused_paths)
针对 21 及以上版本,本方法主要通过在ak.wwise.core.object.get API 的参数中直接使用 WAQL 搜索已使用音频文件的相关信息,要注意的是需要过滤掉返回 result 包含的 plugins 的内容。相较之下,这个方法由于不需对文件进行读取,效率更高。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# 对比\SFX及\Voices路径下的文件列表和项目已使用的文件列表获得未使用资源的列表
def get_unused_paths(used_paths):
unused_paths = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(originals_path + '\\SFX'):
for file in files:
base_name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
if ext == ".wav":
cur_path = os.path.join(root, file)
cur_path_lower = cur_path.lower()
if used_paths.count(cur_path_lower) == 0:
unused_paths.append(cur_path)
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(originals_path + '\\Voices'):
for file in files:
base_name, ext = os.path.splitext(file)
if ext == ".wav":
cur_path = os.path.join(root, file)
cur_path_lower = cur_path.lower()
if used_paths.count(cur_path_lower) == 0:
unused_paths.append(cur_path)
return unused_paths
在获得了工程中正在使用的音频文件的路径后,对比资源文件夹中全部的音频文件就可以得到未在使用中的文件的路径。
