本文(水一期) Wwise RTPC 插值曲线的复现,契机是项目移植受限,需要手搓部分 Wwise 的特性。在没有源码的参考的情况下想要完全 1:1 复现 Wwise 中的十种曲线,虽然涉及的知识仅限初中数学难度,但做的时候发现这更像一种费时的解谜和体力活…
Wwise RTPC 的 Curve 属性包含了十种类型的插值曲线,这十种曲线在 Authoring 中、wwu 文件内、以及官方文档中的显示名称都自成一派(幽默一致性)。
首先通过 WAAPI ak.wwise.core.object.get 获取到 RTPC 的 Curve 曲线类型,手动测试获取后发现返回值是 string 类型的曲线名称;然而 Action 对象的 FadeInCurve / FadeOutCurve 属性包含其中九种曲线,官方文档给出的数据类型是 int 类型及对应的值,三类显示如下:
| Authoring | 官方文档 | WAAPI |
|---|---|---|
| Logarithmic (Base 3) | 0 - Logarithmic (Base 3) | Log3 |
| Sine (Contant Power Fade In) | 1 - Sine | Log2 |
| Logarithmic (Base 1.41) | 2 - Logarithmic (Base 1.41) | Log1 |
| Inverted S-Curve | 3 - Inverted S-Curve | InvertedSCurve |
| Linear | 4 - Linear | Linear |
| S-Curve | 5 - S-Curve | SCurve |
| Exponential (Base 1.41) | 6 - Exponential (Base 1.41) | Exp1 |
| Sine (Contant Power Fade Out) | 7 - Reciprocal Sine | Exp2 |
| Exponential (Base 3) | 8 - Exponential (Base 3) | Exp3 |
| Constant | Constant |
Input
从 WAAPI ak.wwise.core.object.get 返回的曲线信息如下:
"Curve": {
"id": "{261609FF-8104-4BB5-AB07-160DF0A8B534}",
"points": [
{
"x": 0.0,
"y": 11.64929,
"shape": "Log1"
},
{
"x": 3.14717,
"y": 7.6169,
"shape": "Linear"
},
{
"x": 4.36981,
"y": 0.67505,
"shape": "Exp2"
},
{
"x": 24.0,
"y": 11.649,
"shape": "SCurve"
}
],
"@Flags": 3
},
各个点的 shape 属性表示该点和下一相邻点之间的插值曲线类型(最后一个点忽略),因此要根据 x (GameParameter 的值)计算 y (对应属性值),需要先判断 x 位于哪两个点之间,再将两点坐标信息及 x 的值代入下面的函数中计算 y 的值。
Log & Exp
在 GeoGebra 中画了半天各种对数和指数函数,最终怎么都无法和 Authoring 中的曲线图拟合,最后崩溃发现它们的真面目竟然都是幂函数…
总之经过反复试错,这两大类共 4 种曲线(Log3,Log1,Exp3,Exp1),是由幂函数在以起止点框定的限定值域下,通过横纵放缩将基函数恰好放入以起止点为斜边的矩形中,最后经过平移、翻转变换得来的,曲线图如下:
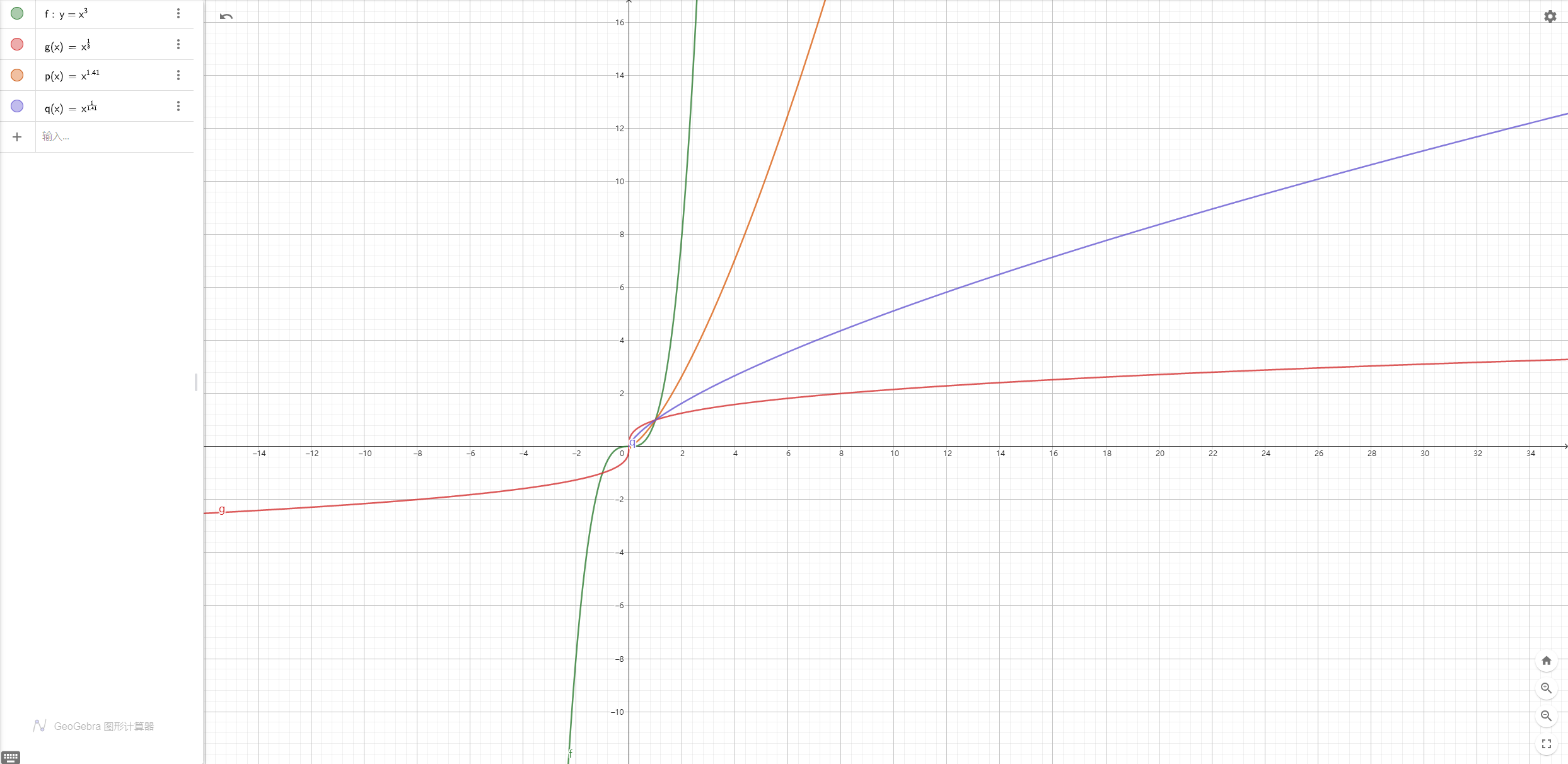
Exp3
基函数: y = x^3 x ∈ [0, t] t = |y2 - y1|
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public static float Exp3(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Exponential (Base 3)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(x2 - x1);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(y2 - y1);
float scale = Mathf.Pow(abs_x, 3) / abs_y;
if (y2 - y1 < 0)
{
return -Mathf.Pow((x - x1), 3) / scale;
}
else
{
return Mathf.Pow((x - x1), 3) / scale;
}
}
Exp1
基函数: y = x^1.41 y ∈ [-t, 0] t = |y2 - y1|
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public static float Exp1(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Exponential (Base 1.41)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(x2 - x1);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(y2 - y1);
float scale = Mathf.Pow(abs_x, 1.41f) / abs_y;
if (y2 - y1 < 0)
{
return -Mathf.Pow(Mathf.Abs(x - x1), 1.41f) / scale;
}
else
{
return Mathf.Pow(Mathf.Abs(x - x1), 1.41f) / scale;
}
}
Log3
基函数: y = x^1/3 y ∈ [0, t] t = |y2 - y1| (Exp3 的反函数)
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public static float Log3(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// # Logarithmic(Base 3)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float delta_x = x2 - x1;
float delta_y = y2 - y1;
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(delta_x);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(delta_y);
float scale = Mathf.Pow(abs_x, 3) / abs_y;
float adjustedX = x - x1 - delta_x;
if (delta_y < 0)
{
return -Mathf.Pow(adjustedX, 3) / scale + delta_y;
}
else
{
return Mathf.Pow(adjustedX, 3) / scale + delta_y;
}
}
Log1
基函数: y = x^1/3 y ∈ [0, t] t = |y2 - y1| (Exp1.41 的反函数)
由于该函数定义域不能小于 0,手动定义一函数使其定义域和值域与基函数相反,再根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
public static float Log1(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Logarithmic(Base 1.41)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float delta_x = x2 - x1;
float delta_y = y2 - y1;
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(delta_x);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(delta_y);
float scale = Mathf.Pow(abs_x, 1.41f) / abs_y;
float adjustedX = x - x1 - delta_x;
float absAdjustedX = Mathf.Abs(adjustedX);
float result = Mathf.Pow(absAdjustedX, 1.41f) / scale;
if (delta_y < 0)
{
if (adjustedX < 0)
{
return result + (y2 - y1);
}
else
{
return -result + (y2 - y1);
}
}
else
{
if (adjustedX < 0)
{
return -result + (y2 - y1);
}
else
{
return result + (y2 - y1);
}
}
}
Sine
接着我们将得出另一著名的 Wwise 等式: Sine = Log2。和上面类似,只不过由于 Sine 的值域限制,这里需要先额外进行一次 y 轴缩放,再进行 x 轴缩放。
Sine
基函数: y = sinx x ∈ [0, pi/2]
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public static float Exp2(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Sine (Constant Power Fade out)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float delta_x = x2 - x1;
float delta_y = y2 - y1;
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(delta_x);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(delta_y);
float normalizedPosition = Mathf.PI / 2 * (x - x1 - delta_x) / abs_x;
float sineValue = Mathf.Sin(normalizedPosition);
if (delta_y < 0)
{
return -abs_y * sineValue + delta_y;
}
else
{
return abs_y * sineValue + delta_y;
}
}
Reciprocal Sine
基函数: y = sinx x ∈ [-pi/2, 0]
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行放缩和翻转得到。
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public static float Log2(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Sine (Constant Power Fade in)
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float delta_x = x2 - x1;
float delta_y = y2 - y1;
float abs_x = Mathf.Abs(delta_x);
float abs_y = Mathf.Abs(delta_y);
float normalizedPosition = Mathf.PI / 2 * (x - x1) / abs_x;
float sineValue = Mathf.Sin(normalizedPosition);
if (delta_y < 0)
{
return -abs_y * sineValue + y1;
}
else
{
return abs_y * sineValue + y1;
}
}
Constant & Linear
最简单的一集,注意左闭右开边界判定。
Constant
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public static float Constant(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Constant
if (x != x2)
{
return y1;
}
return y2;
}
Linear
拟合度: 100%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public static float Linear(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Linear
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float deltaX = x2 - x1;
float deltaY = y2 - y1;
float slope = deltaY / deltaX;
if (deltaY < 0)
{
return -slope * (x - x1) + y1;
}
else
{
return slope * (x - x1) + y1;
}
}
SCurve
由于 Sigmoid 函数的类型太多,无法一一试验,选择调整最常见的 Logistic 的系数来进行拟合,这部分的结果没有完全拟合 Wwise 官方的插值曲线。
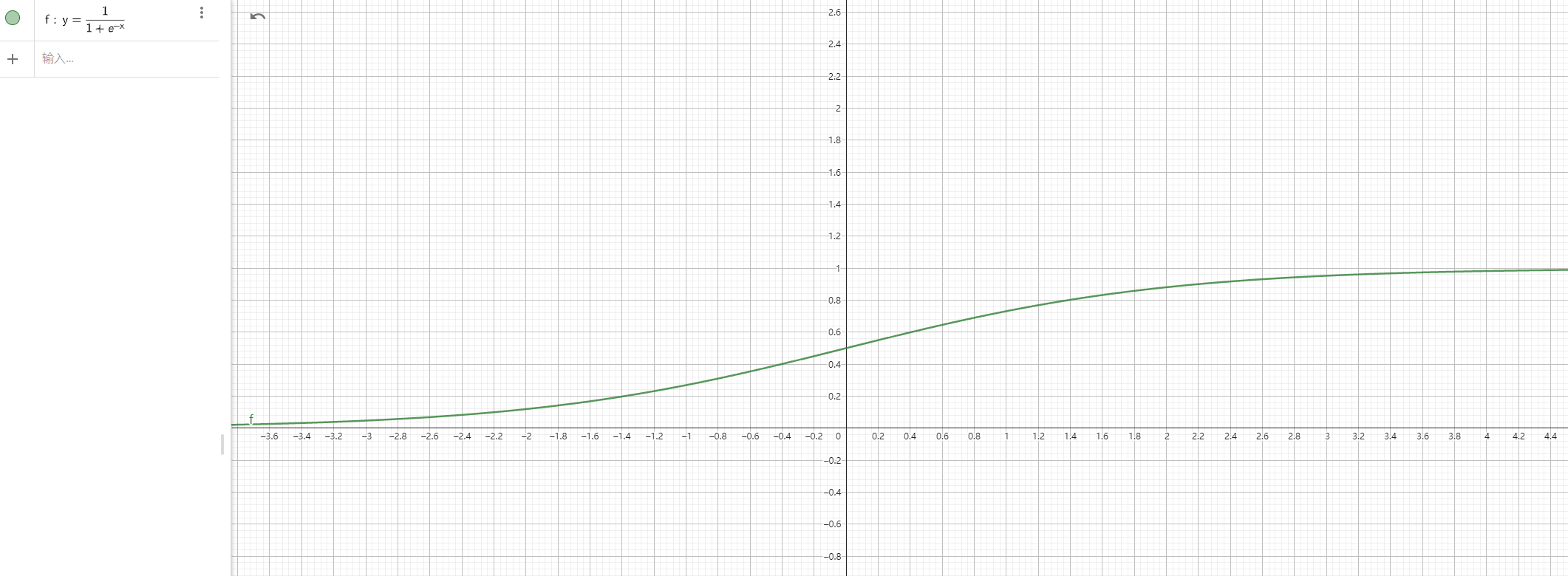
SCurve
基函数: y = 1 / (1 + e^(-5.89*x))
根据起止点的坐标对基函数进行平移和翻转得到。由于 Logistic 的值域为 (0, 1),对于两个边界条件还需手动判定,而整体曲线一定不光滑,趋近边界的部分一定会有突变,这一点在放大 Wwise Authoring 中的曲线后也能得到印证。
拟合度: 80%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public static float SCurve(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// S-Curve
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float mid_x = (x1 + x2) / 2;
float scale_x = (x2 - x1) / 2;
float t = (x - mid_x) / scale_x;
float logistic_value = 1 / (1 + Mathf.Exp(-5.89f * t));
return (y2 - y1) * logistic_value + y1;
}
InvertedSCurve
基函数: y = 1 / (1 + e^(-3.5*x))
经观察可以发现 InvertedSCurve 实际上是将 SCurve曲线从 x = 0 处分开并将最左和最右端重新拼接,两者的一阶导变化趋势正好相反。根据基函数做一个值域的重新映射即可实现,但问题在于需要对中点处进行一次额外判定,因为此时两端的突变来到了中心点左右。在 Wwise Authoring 中的曲线不存在此问题,有更好的实现请大家多交流。
拟合度: 80%
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public static float InvertedSCurve(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x)
{
// Inverted S-Curve
float ori_x = x;
if (x == x1)
{
return y1;
}
if (x == x2)
{
return y2;
}
float delta_x = x2 - x1;
float delta_y = y2 - y1;
float mid_x = (x1 + x2) / 2;
float scale_x = (x2 - x1) / 2;
if (x < mid_x)
{
x = x + delta_x / 2;
}
else if (x > mid_x)
{
x = x - delta_x / 2;
}
else
{
return delta_y / 2 + y1;
}
float t = (x - mid_x) / scale_x;
float logistic_value = 1 / (1 + Mathf.Exp(-3.5f * t));
if (ori_x < mid_x)
{
return (y2 - y1) * logistic_value + y1 - delta_y / 2;
}
else
{
return (y2 - y1) * logistic_value + y1 + delta_y / 2;
}
}
响度——非线性变化的 y 轴
参数驱动响度变化的 RTPC 在绝大多数情况下都会使用非线性变换的 y 轴,虽然如此,但目的却是为了模拟出事实上线性的响度变化以符合人耳真实的听觉感受变化。为此我们需要根据下图通过 (0, -200) 和 (100, 0) 的直线和曲线,对上述函数计算求得的 y(响度值)做一变换,来映射至非线性变换的 y 轴中。
直线函数: y = 2 * (x - 100)
曲线函数: y = 20 * log10(x / 100)
由于上述直线和曲线的仿射不变性,因此不必考虑定义域改变带来的变化。
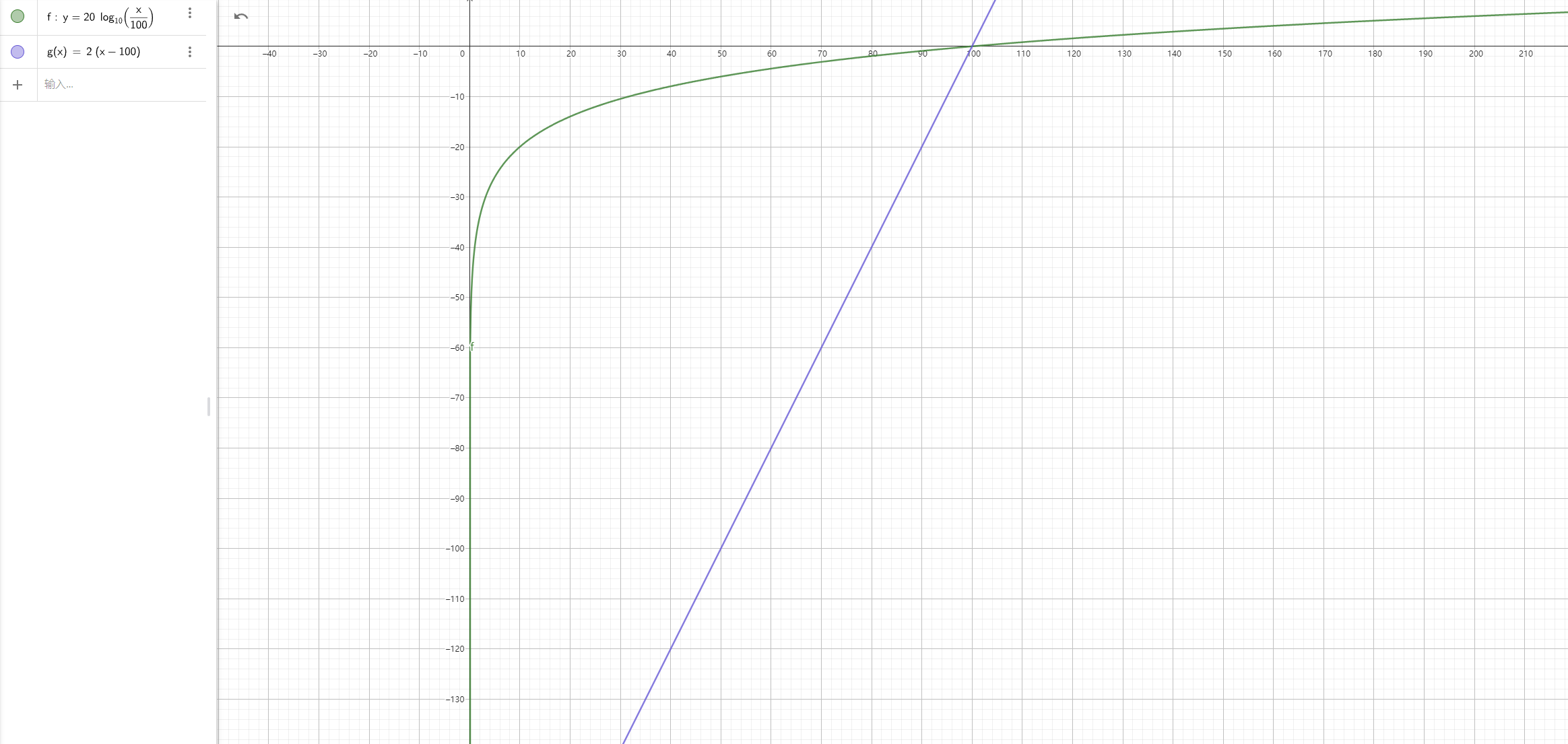 具体函数如下,t 为上述函数求得的 y 值:
具体函数如下,t 为上述函数求得的 y 值:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public static float YScalingChange(float t)
{
if (t > 0)
{
t = -t;
}
float argument = (t / 2.0f + 100.0f) / 100.0f;
float log10Result = Mathf.Log(argument) / Mathf.Log(10);
float result = 20 * log10Result;
if (t > 0)
{
result = -result;
}
return result;
}